Causes of Dementia
Dementia is caused by gradual changes and damage in the brain. The most common causes
of dementia include diseases in which the brain cells degenerate and die more quickly
than they would as part of the normal ageing process. This damage interferes with
the ability of brain cells to transmit information. When brain cells
are unable to communicate, a person's thought processes, behaviour and emotions
can be affected.
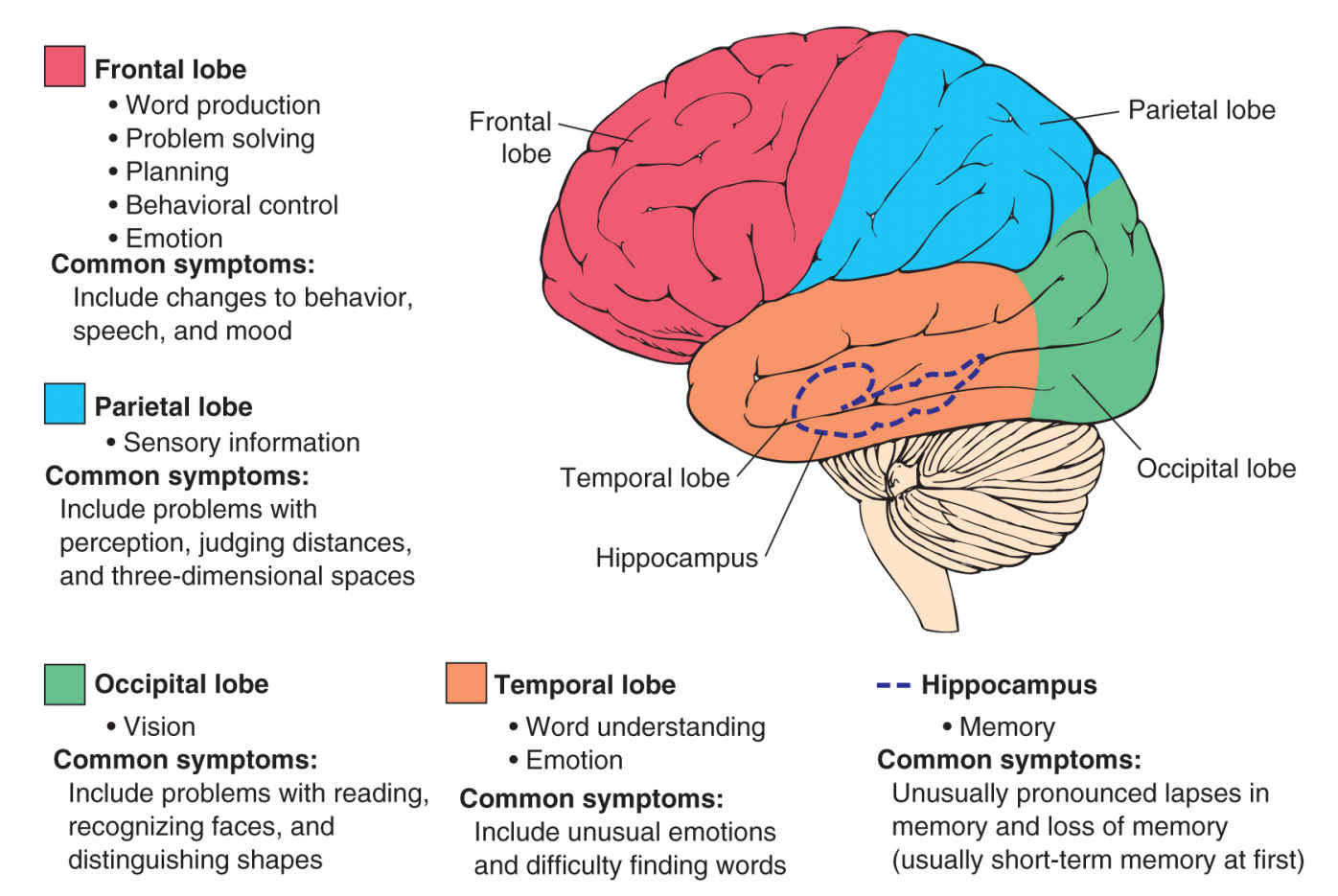
The brain has many distinct regions, each of which is responsible for different
functions. When cells in a particular region are damaged, that region is unable
to perform its task normally. The figure below depicts the region of the brain and
its responsibility together with the associated symptoms when cells in the region
are damaged.
Source:
Neupsykey
While most damages to the brain that causes dementia are irreversible and get worst
over time, thinking and memory problems caused by the conditions below may improve
when appropriate treatment are administered:
- Depression
- Medication side effects
- Excess use of alcohol
- Thyroid problems
- Vitamin deficiencies
Types of Dementia
The common types of Dementia are Alzheimer's disease, Vascular Dementia, Dementia
with Lewy bodies and Fronto-temporal Dementia. Click on the respective factsheets
to learn about their symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and support